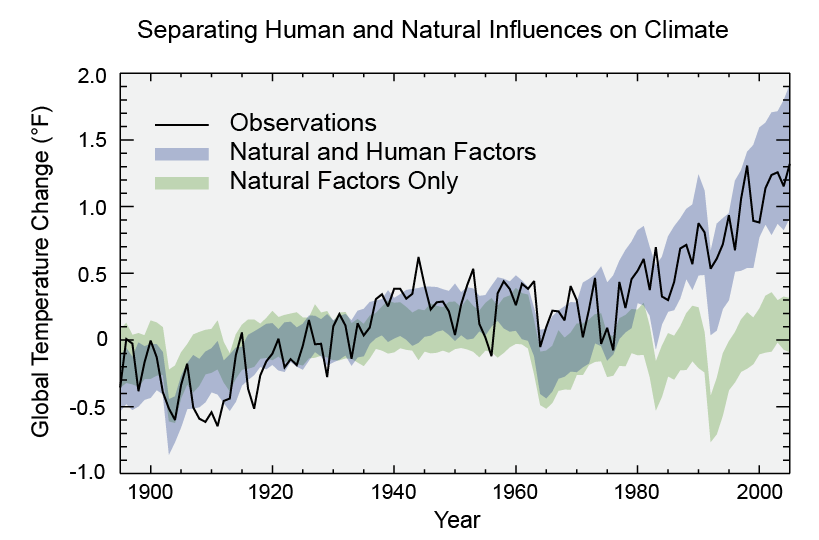
The evolution of industry through time has always been a caused of changes at economy levels. From the very first beginning industrial revolution promoted alterations: economic activities in many communities moved from agriculture to manufacturing, production shifted from its traditional locations in the home and the small workshop to factories, the overall amount of goods and services produced expanded dramatically and the proportion of capital invested per worker grew, new groups of investors, businesspeople and managers took financial risks and reaped great rewards.
“The future is not preordained by machines. It’s created by humans.” These are the words of Erik Brynjolfsson, director at the MIT Initiative on the Digital Economy. Nevertheless, it is undeniable that the continuing automation and digitization of our world and our workplace is a seismic shift. The truth is that the reality is changing, and the society should accompany with it. The job market is one of the many areas that need to embrace the development in a way to stabilize and contribute to a healthy economy.
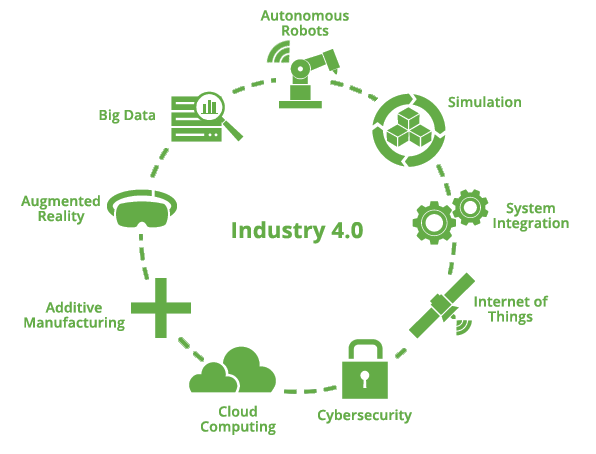
The Industry 4.0 will and already is also causing several changes on areas such as economic development or employment. With this technology revolution business and management can become more accurate and predicitve as well as the consequences that come from them. Given this, it is expected with the improvement of technology and the help of new tools and methods such as Internet of Things (IoT) or Machine Learning the following benefits:
- Profit promotion
- Job creation
- Consumer attraction
- Cost reduction
- Anticipation and risk management
- Pursuit of competitiveness over time
Apart from that, the 4th Industrial Revolution will also change the way work is done in very distinctive factors:
- It is breaking down the traditional silos that separate the different departments within a business, so that with real time time information they can optimize conditions and improve orders and production output. In short, sharing data makes manufacturing more agile, bringing the days of moving in silos to an end.
- It is dawning a new age of personalised manufacturing, combining customised production with the speed and on-time delivery expectations of today’s consumers. Intelligent and integrated systems play a vital role for manufacturers that want to put their customers first, delivering instructions to machines about specific customer orders as they progress along the production line, in an inversion of normal manufacturing.
- It requires a cultural change in the way humans work with machines. Not only will employees be able to work closer across different departments in an Industry 4.0 world, sharing real-time data and insights to make accurate decisions in the workplace, they will also be able to have some of their tasks automated by machines, allowing them to work on new, less tedious tasks instead, and crunching delivery timescales.

In brief, there is a generic consensus that attitudes and special vision need to shift, as manufacturers break down barriers between departments, embrace customisation and work in tandem with machines. It is up to employers and their teams alike, to embrace these changes and change their mindsets, as they grow their businesses in the Industry 4.0 world.
References: